Kubernetes, also known as K8s, is an open-source system for automating deployments, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Kubernetes helps ensure high availability and fault-tolerance for applications. It is designed to run on a cluster of servers, allowing you to easily scale your Kubernetes cluster.
A Kubernetes cluster consists of a number of worker machines, called 'worker nodes' (usually referred to simply as nodes). These are virtual machines that run containerized applications. Each Kubernetes cluster contains at least one worker node.
Worker nodes host Pods, the smallest units within a Kubernetes cluster. A pod is a group of one or more containers that share resources such as storage and network. The status of Pods is managed through Kubernetes Deployments. See also our 'hello node' tutorial for a quick understanding of working with Deployments and Pods.
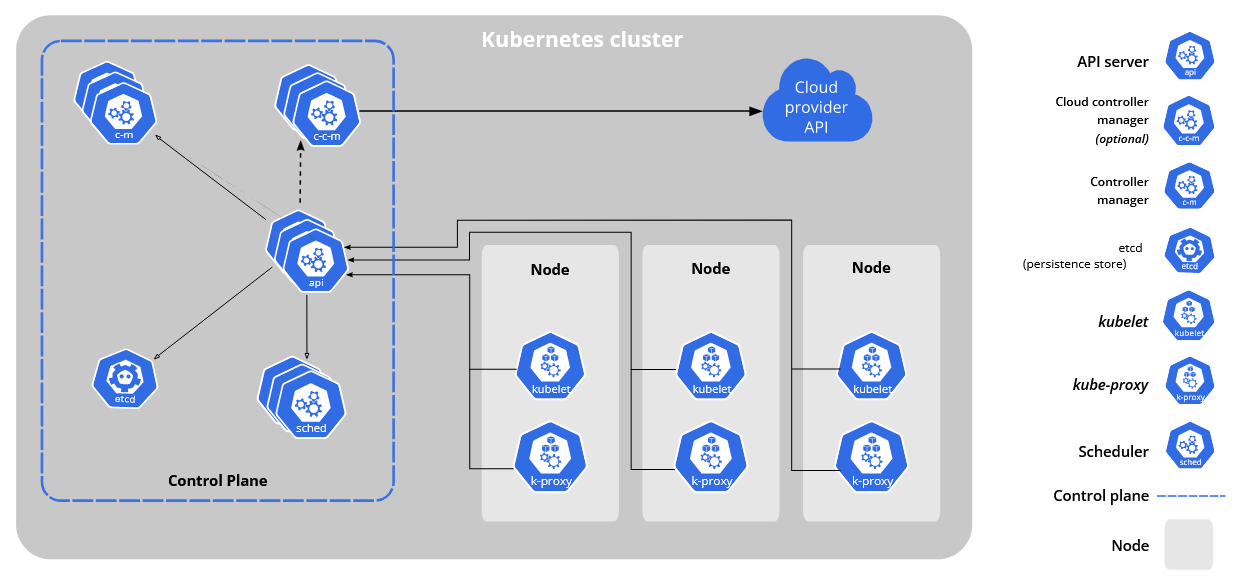
In its most basic components, a Kubernetes cluster consists of a Control Plane (which is managed by us on the redundant TransIP Kubernetes platform) and nodes, as shown in the overview below: