A cronjob is essentially a Unix command that executes a script or program on a specific time or date. Cronjobs are mostly used for retrieving email, sending email and update checks.
You can easily create cronjobs using the web hosting packages of TransIP. Although this does not work based on Unix commands, you can use these cronjobs to periodically execute PHP scripts and programs.
This article shows you how to configure cronjobs in your control panel using a web hosting package.
Creating cronjobs
Log in to the control panel and click 'Shared Hosting' in the menu. Next, select your domain below 'Products'.
Click 'Advanced' at the top, followed by 'Cronjobs'.
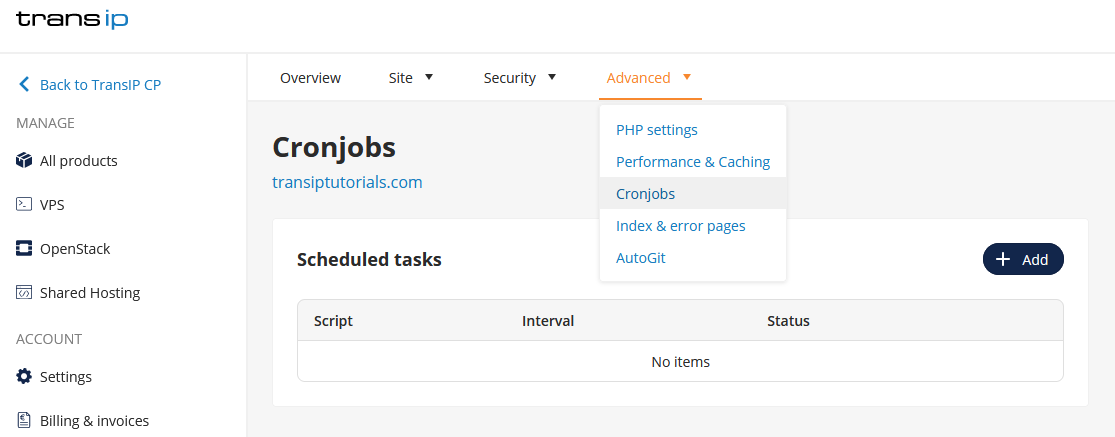
Here you will find an overview of your created cronjobs. To create a new cronjob, click the button '+ Add'.
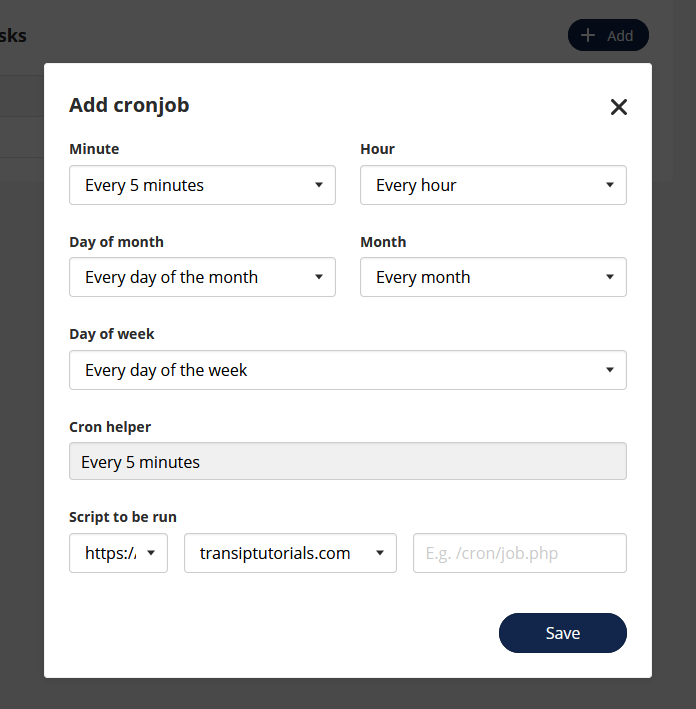
When creating a cronjob, you need to fill in the following information:
- The frequency of the cronjob
- The URL where the script is located
Click on 'Save' to activate your cronjob.
Creating Cronjobs via SSH
You can also add cronjobs via SSH. The advantage of this is that there is less delay, and the script can run longer (20 minutes) than when you set up a cronjob via the control panel (5 minutes).
To schedule cronjobs, you use a crontab. You can open the crontab with:
crontab -eEvery cronjob you create in the crontab is set up on a single line and consists of two parts: one part specifying when the command should be executed, and another part specifying which task should be run:
* 0 * * * your_command_or_script
- Replace
your_command_or_scriptwith a shell script or command, for example:
5 * * * * /usr/bin/php /site/www/script.php
# or:
* - The asterisks indicate when the cronjob will be executed. In the above example, the
0means the command will be executed every day at midnight (0:00). The asterisks in a cronjob represent the following values:
# ┌───────────── minute (0 - 59)
# │ ┌───────────── hour (0 - 23)
# │ │ ┌───────────── day of the month (1 - 31)
# │ │ │ ┌───────────── month (1 - 12)
# │ │ │ │ ┌───────────── day of the week (0 - 6) (Sunday to Saturday)
# │ │ │ │ │
# │ │ │ │ │
# │ │ │ │ │
# * * * * * your_command_or_script After entering your cronjob, exit by pressing 'escape', followed by:
:wqYou can check your set cronjobs with the command:
crontab -l




