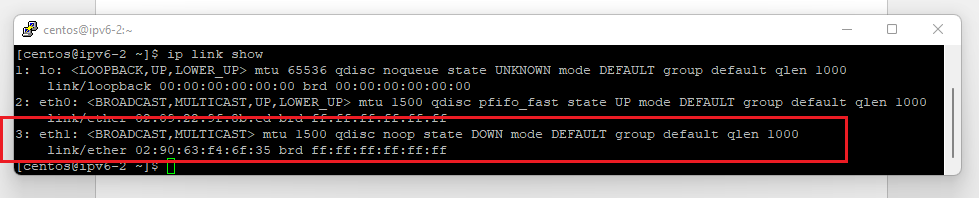
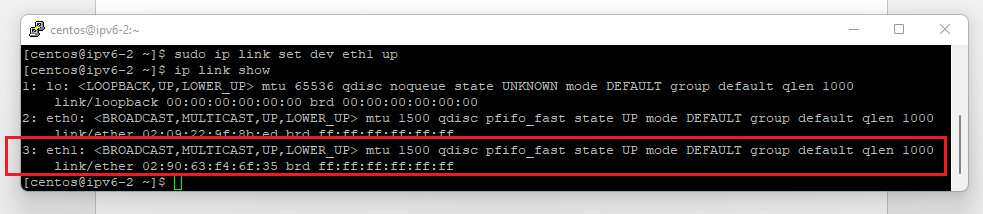
This tutorial will show you how to use an IPv6 address alongside your IPv4 address on your OpenStack instance. Please note that while creating an OpenStack instance it is also possible to automatically assign an IPv6 address.
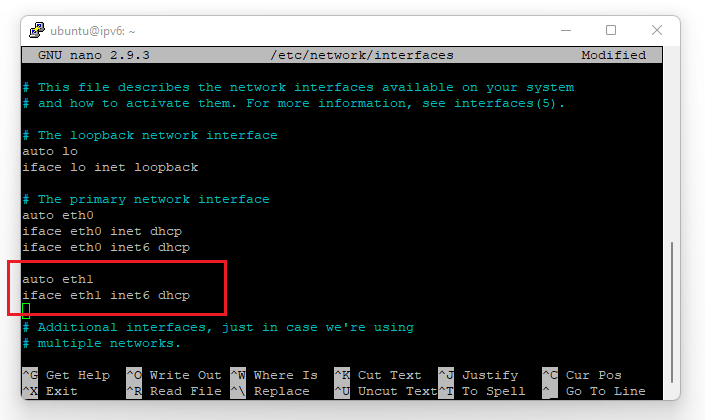
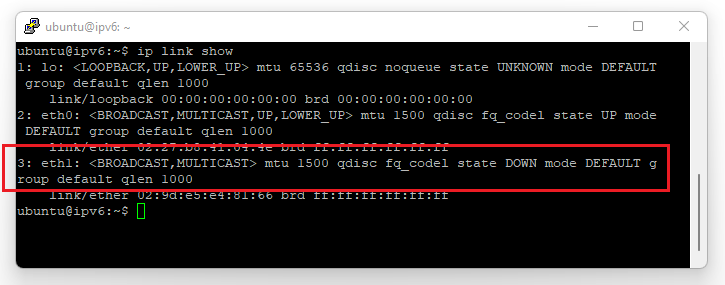
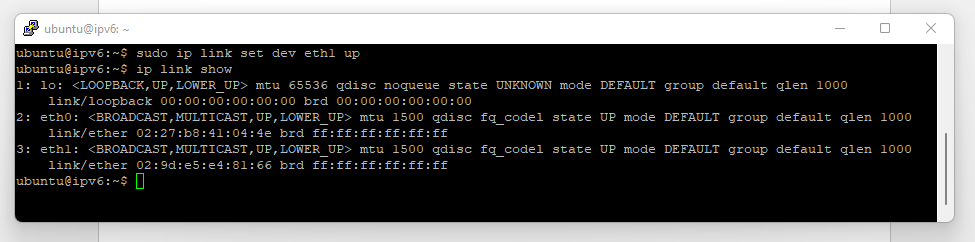
In OpenStack, you cannot set an IPv6 and IPv4 address on the same interface simultaneously. In this tutorial, you'll create a second interface to which you'll attach the IPv6 address.
This tutorial is written for the following operating systems:
- Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, and Debian 11
- Ubuntu 18.04 and Debian 10
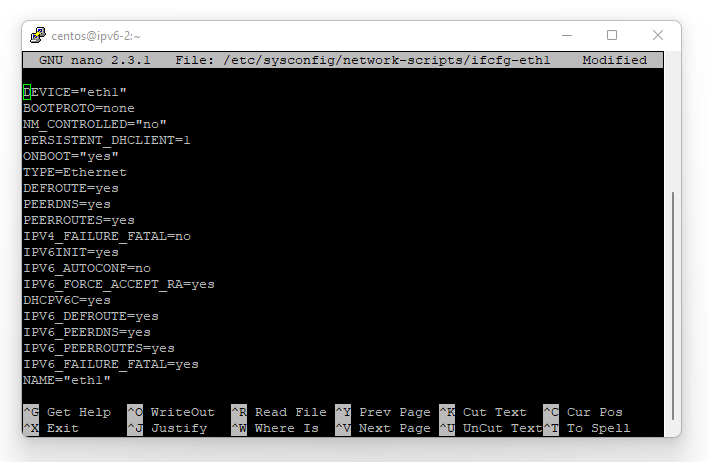
- CentOS 7+, Alma Linux 8+, and Rocky Linux 8+
- Windows (from 'Windows Server 2016')
Step 1
Log in to the Horizon web interface of OpenStack, and in the left menu under 'Compute', click on 'Instances'.
Step 2
To the right of the instance, under 'Actions', click the down arrow. In the drop-down menu, click 'Attach Interface'.
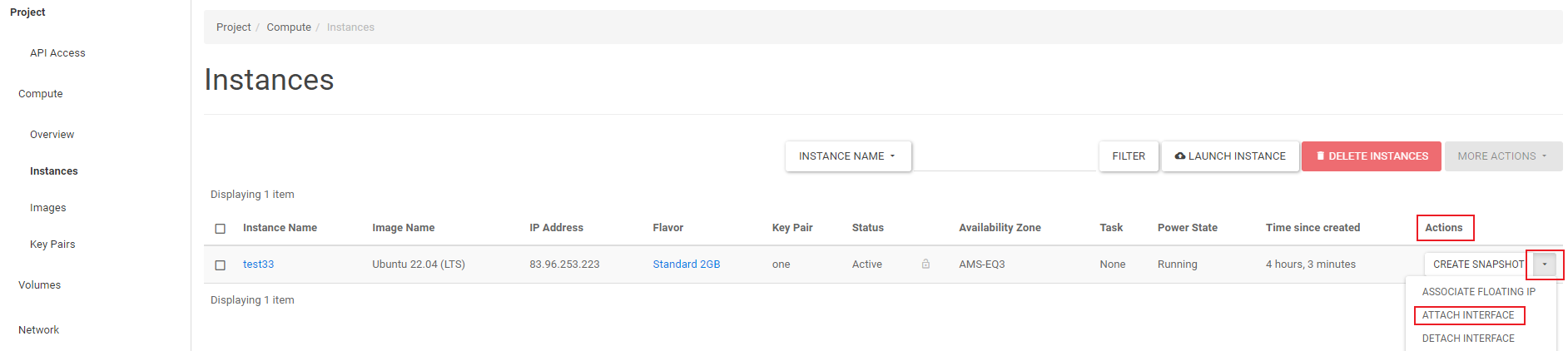
Step 3
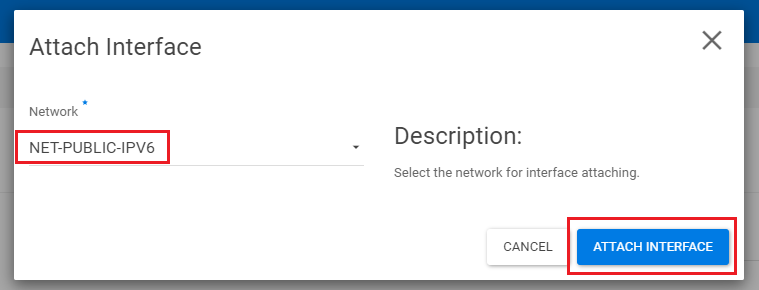
Click the down arrow next to 'Select Network' and select 'net-public-ipv6' from the drop-down menu.
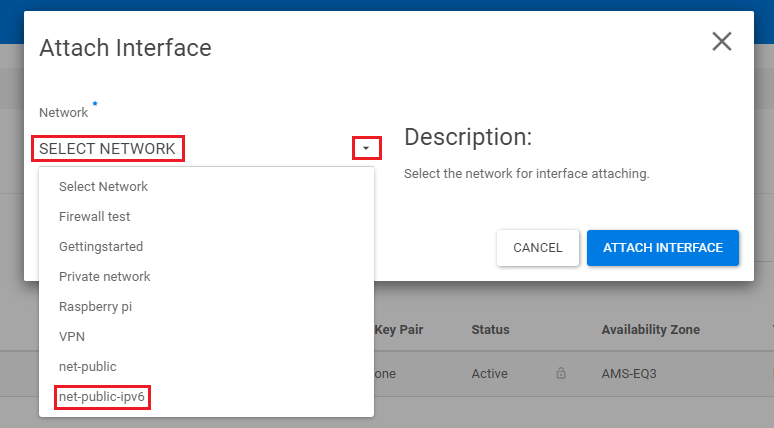
Step 4
You will now see 'Network net-public-ipv6' below. Click 'Attach Interface' at the bottom right to attach the interface to the instance.
Step 5
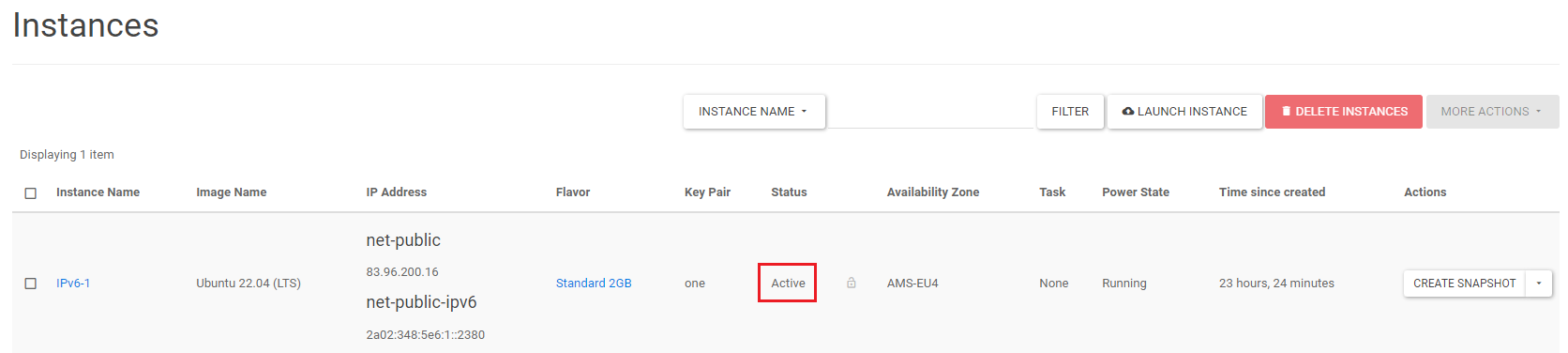
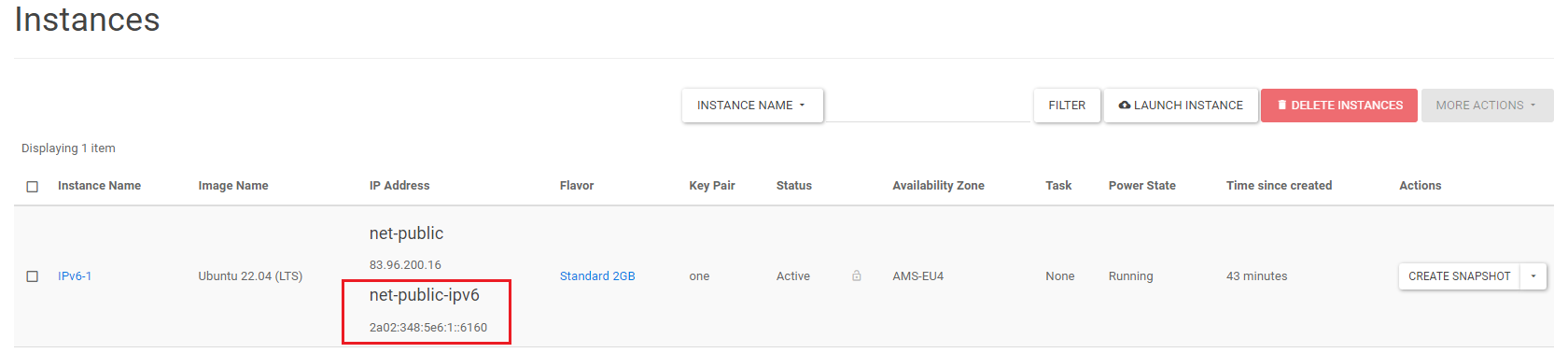
The IPv6 address is now attached to the instance. You will see the IPv6 address (net-public-ipv6) listed alongside your IPv4 address (net-public).
Configuring IPv6 on Your Instance
Step 1
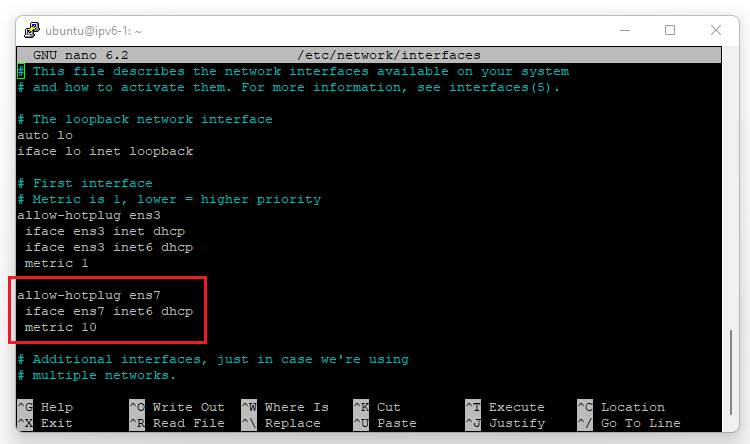
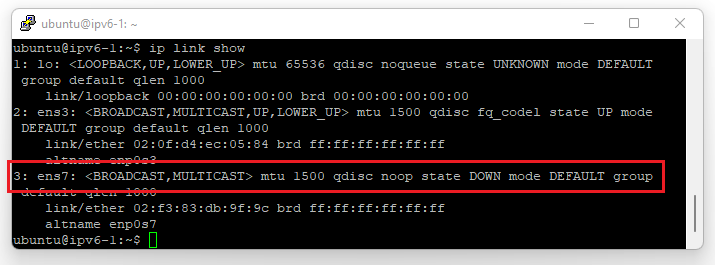
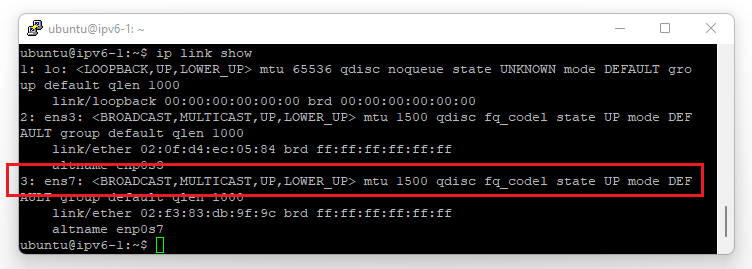
First, configure the IPv6 address on your instance. For Linux distributions, click the arrow next to your used distro/operating system, or use one of our guides for configuring the IP address of your instance on our VPS platform. See this overview.
For Windows Server installations, go directly to Step 2. Windows Server 2016 and later versions will automatically add the second interface.
Since the new IPv6 address doesn't automatically include existing security groups, you need to re-add the security groups to the instance to get the IPv6 address working.
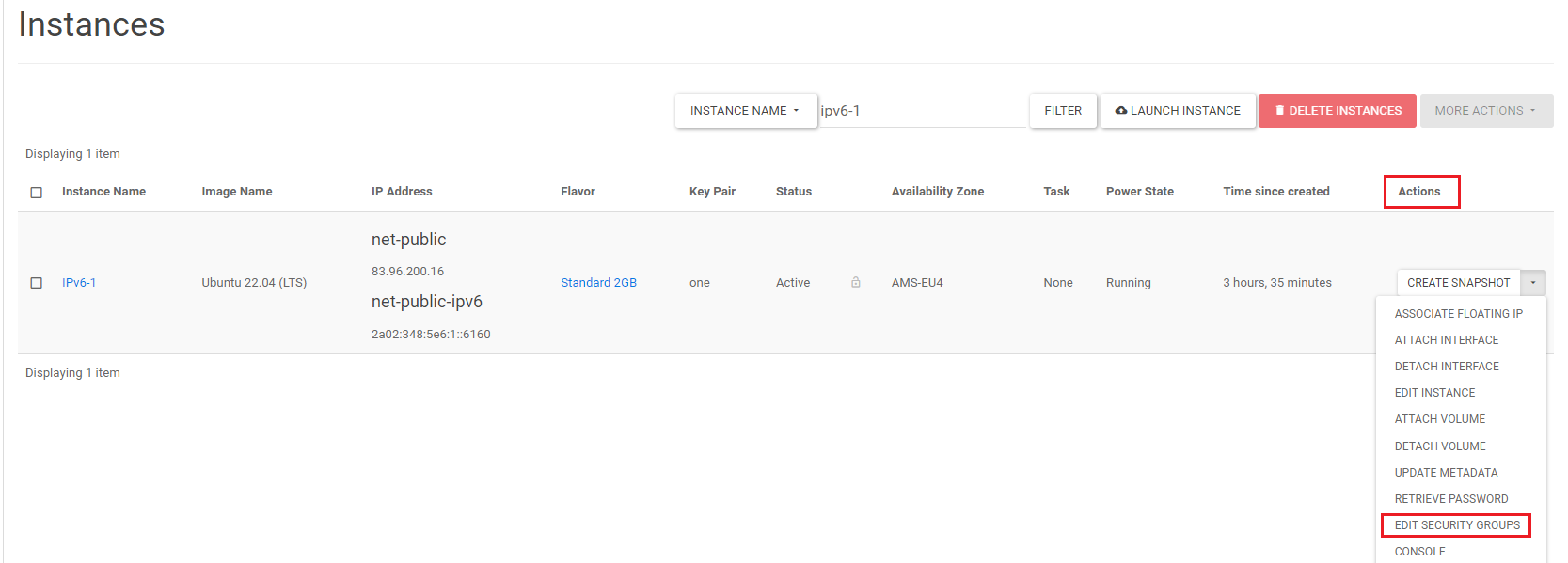
On the right side of the instance under 'Actions', click the downward arrow, then click 'Edit Security Groups' in the dropdown menu.
Step 3
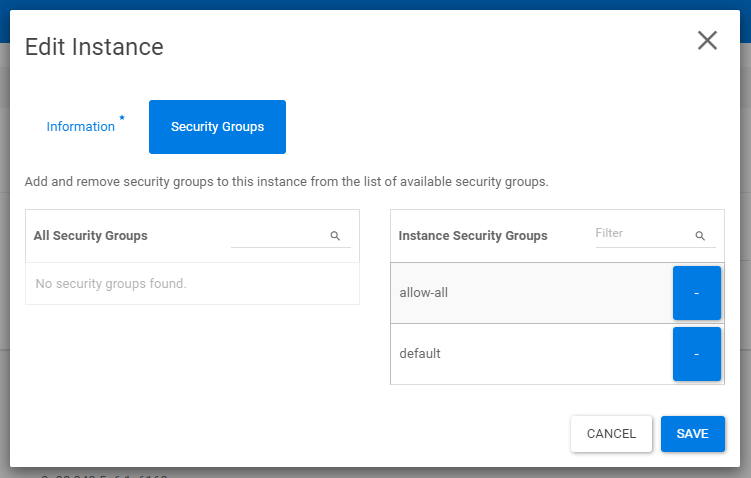
A pop-up titled 'Edit Instance' will appear. Click 'Save' to re-add the security groups.
Step 4
To apply the changes to the instance, it needs to be rebooted. Save your work and shut down the instance from the operating system's command line.
On the right side of the instance under 'Actions', click the downward arrow. Then click 'Soft Reboot Instance' in the dropdown menu.
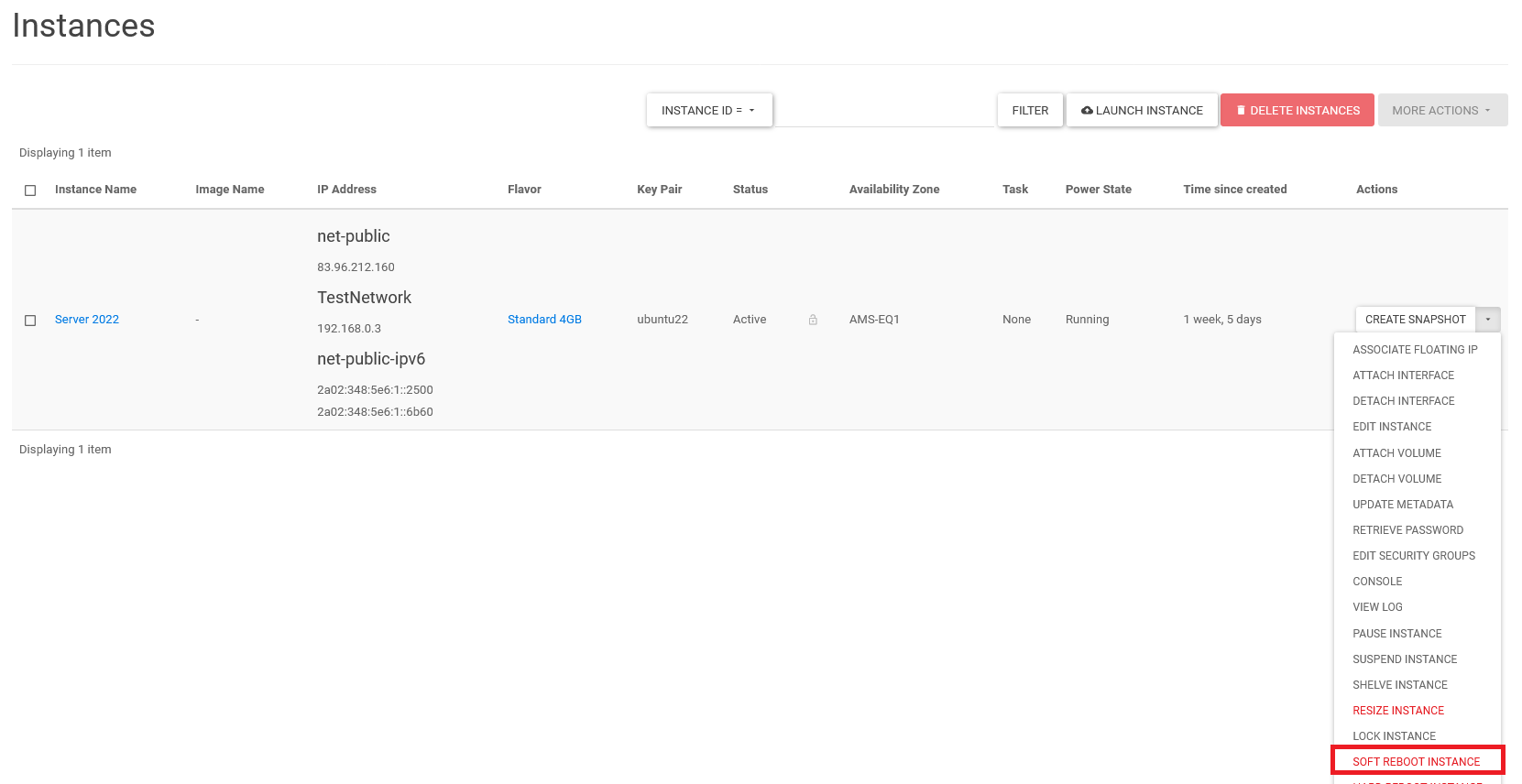
Step 5
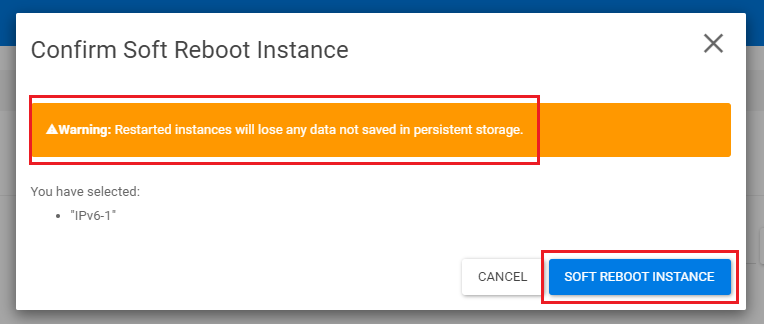
In the confirmation window at the bottom-right, click the 'Soft Reboot Instance' button in the pop-up to restart the instance. The 'Warning' indicates that if you haven't saved the changes, they will be lost. If you've followed all the steps in this guide carefully, you can ignore this warning.
Below the 'Reboot Started' bar, you will see that the instance is booting up. In most cases, the reboot process will take up to half a minute.
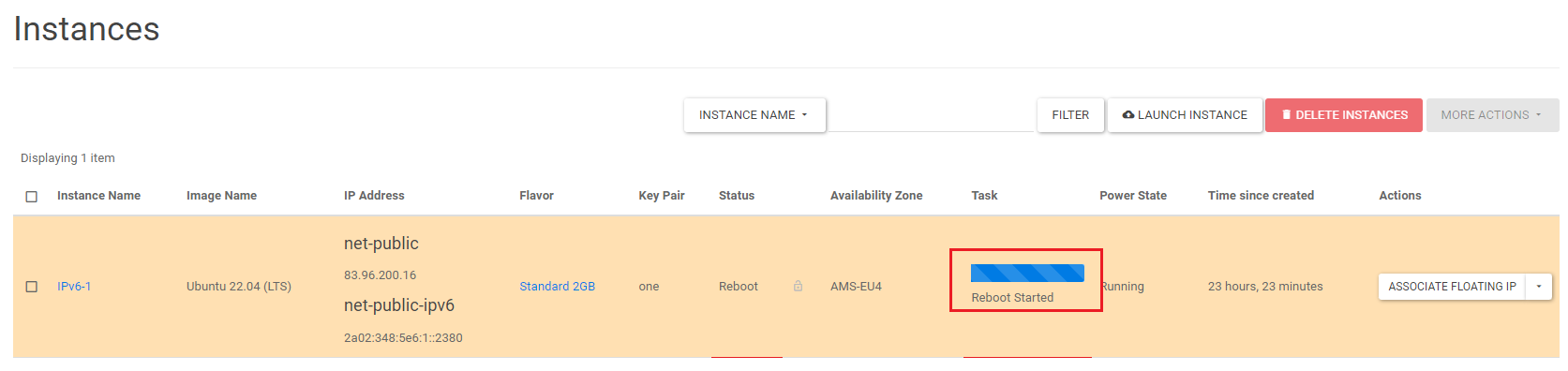
Once this process is complete, the instance will be back to the 'Active' state and ready to use. Congratulations! You now have a working IPv6 address on your instance.