In this article, we explain how to set a TXT record within the DNS settings of your domain name.
TXT is an abbreviation for Text and unlike other DNS records, it does not point to a location. The TXT record is intended to give information to the server that requests the TXT record.
Where do I add a TXT record?
You can add all your DNS records easily and free of charge via your control panel. Go to 'Domain' and select the domain in the left column for which you want to set the TXT record (don't check the box).
Now scroll to 'Advanced Domain Settings', followed by 'DNS'. If you do not see this yet, first click the switch behind 'TransIP settings' so the TransIP settings are switched off. The DNS records of your domain name will become visible, after which you can change them at will.
How do I set a TXT record?
There are several applications of the TXT record, of which the so-called SPF and DKIM records are the most used applications.
- Read the article 'Entering DNS records and nameservers via the control panel' for more information on setting DNS records.
- Read the article 'Setting an SPF record' for more information on configuring an SPF record.
- Read the article 'Setting a DKIM record' for more information on configuring an SPF record.
DMARC
Another application for TXT is the DMARC record. This type of record can be used to indicate that emails are protected by SPF or DKIM and tells the receiving mailserver what to do if none of these methods succeed.
This type of record is an extra security measure but is not used very often. Check out this page for more information on DMARC.
Below you can see an example of what a DMARC record looks like in the control panel.
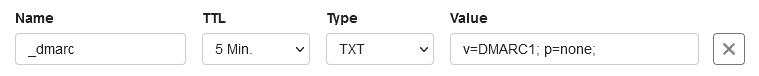
The value of the DMARC record must always start with the 'v' tag and must also always contain the 'p' tag. Tags are separated with a ';'.
- 'v' indicates the version of DMARC, which is always DMARC1.
- 'p' stands for policy and indicates what the recipient should do with emails that do not pass the DMARC check. The possible policies are none, quarantine, and reject.
- None = No specific action is taken regarding message delivery.
- Quarantine = Emails that fail the CMARC check are considered suspicious. Depending on the recipient, this may mean that the email is placed in the spam ffolder, or is flagged as suspicious.
- Reject = Emails that fail the DMARC check should be rejected.
- You can choose to have a collection of feedback sent to a desired email address. This is indicated with the 'rua' tag (reporting URI aggregate). For example 'rua=example@domainname.com'.
- If the domain in the rua tag is not the same as the domain on which you set the DMARC record, the receiving domain must include a verification record (type TXT) in the DNS with name 'example.com._report._dmarc' and value 'v=DMARC1'. Replace 'example.com' with the domain name for which the DMARC record applies.
All tags and their possible contents can be found in RFC 7489.
TXT records for validation purposes
A different application of TXT is the valitdating various web applications, such as the 'Google site verification'. Check out this page from Google for more information on this procedure. Below is an example of a TXT record that includes Google site verification.

This article has discussed the setting of a DKIM record. For a general explanation about DNS records and entering them, see the article ‘DNS and nameservers'.
If you want to know more about setting DNS records for your Web Hosting service, use the article 'The DNS settings of my web hosting package'.




