Open DNS resolvers are DNS resolvers that respond to each IP address and can, therefore, be abused for "amplification attacks". Simply put, an amount of data can be sent to your DNS resolvers (from a spoofed IP) and a significantly larger amount of data is returned. In this way, malicious people can then misuse your resolvers to perform a (D)DoS attack on the spoofed IP address.
That is why it is very important that you always disable this and only allow resolving for specific IPs / servers, for example from your private network. You can disable the open DNS resolvers as follows:
Windows Server
Alternatively, instead of the instruction below, you can use the inbound rules of your Windows Firewall with Advanced Security> DNS (TCP, Incoming & UDP, Incoming)> Scope> Remote IP addresses to only allow 127.0.0.1, the IP of your VPS and the IPs on your private network.
Step 1
Log in to your server and click 'DNS' in your Server Manager with the left mouse button. Then click the name of your VPS with the right mouse button and click 'DNS Manager'.
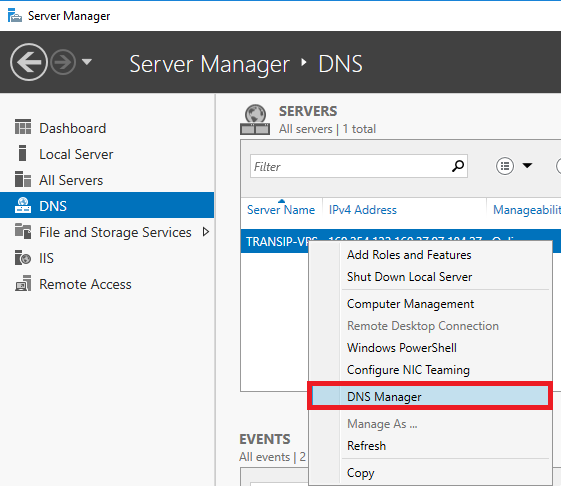
Step 2
DNS management is opened. Click the name of the VPS with the left mouse button in the left menu and then 'Properties' with the right mouse button (directly clicking the name of the VPS with the right mouse button does not work).
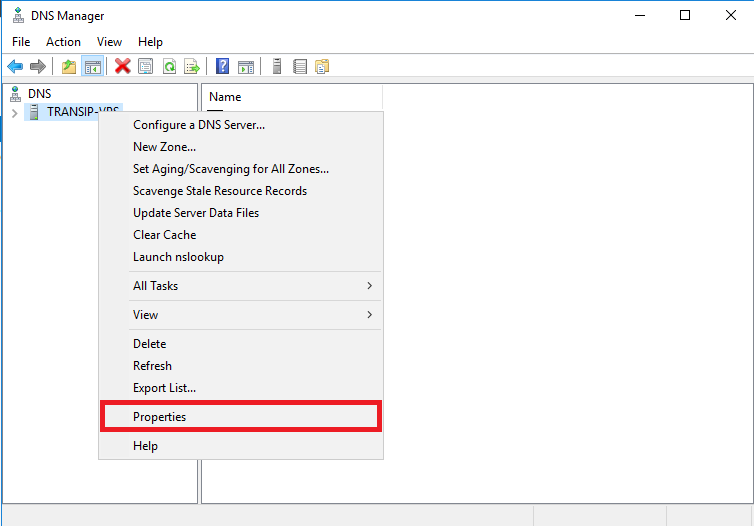
Step 3
Click the 'Advanced' tab (see the screenshot in step 4).
Step 4
Check 'Disable recursion' and click 'Apply'.
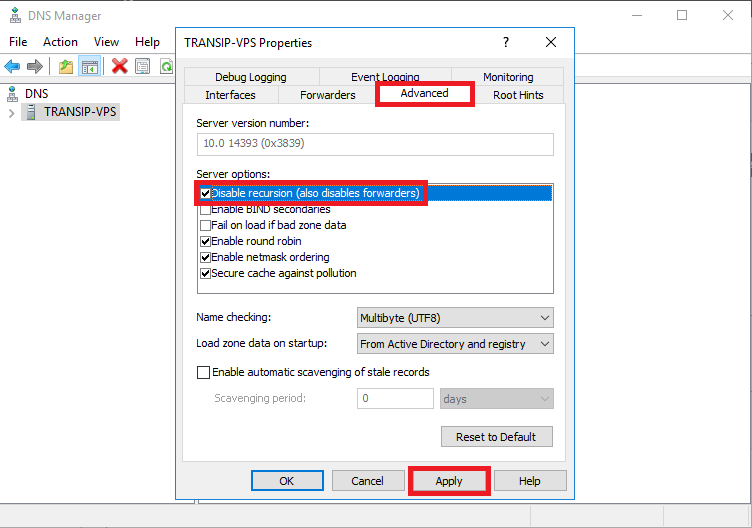
Open DNS resolvers on your VPS are now disabled.
Linux
BIND is most commonly used as a DNS server, but if you use a different DNS server, please consult its documentation. In Bind you disable open DNS resolvers by adding the following lines (as root) in the options section of /etc/named.conf:
Step 1
First open /etc/named.conf:
nano /etc/named.conf
Step 2
Under the 'Options' section, add the lines:
allow-transfer {"none";};
allow-recursion {"none";};
recursion no;
Save the changes and close the file (ctrl + x > y > enter).
Step 3
To process the changes, reloading the service suffices:
Ubuntu / Debian
service bind9 reloadCentOS
service named reload
Should you have any questions left regarding this article, do not hesitate to contact our support department. You can reach them via the ‘Contact Us’ button at the bottom of this page.




