In this article we explain how to set an SSHFP record in the DNS settings of your domain name.
SSHFP is an acronym for Secure Shell fingerprint. The purpose of the SSHFP record is to verify the SSH server's public key through DNS. The fingerprint of the SSH server's public key is used for this, which is published in DNS via the SSHFP record.
The fingerprint is verified using DNSSEC so that the person connecting via SSH does not have to verify it. Usually the fingerprint is accepted blindly by the user in this situation, which makes the connection susceptible for man-in-the-middle attacks.
By using the SSHFP record, this step is not skipped and therefore improves the safety of your SSH connection.
Because DNSSEC is used to verify the fingerprint, it is essential that your domain is secured with DNSSEC.
Domains using the TransIP nameservers are automatically secured with DNSSEC. To set DNSSEC on a domain that uses custom nameservers visit 'How can I secure domains that use custom nameservers with DNSSEC?'.
Where do I add an SSHFP record?
You can add all your DNS records easily and free of charge via your control panel. Go to 'Domain' tab and select the domain in the left column for which you want to set the SSHFP record (don't check the box).
Now scroll to 'Advanced Domain Settings', followed by 'DNS'. If you do not see this yet, first click the switch behind 'TransIP settings' so the TransIP settings are switched off. The DNS records of your domain name will become visible, after which you can change them at will.
After adding and saving your own DNS records, leave the 'TransIP settings' switched off.
How do I set an SSHFP record?
A SSHFP record consists of three parts (divided by a space), in a set order:
- Algorithm, represented by a number.
- Fingerprint type, represented by a number.
- Fingerprint, represented by a string of hexadecimal characters ('0-9' and 'a-f').
An example of an SSHPF record in your control panel for the root domain is shown in the image below:
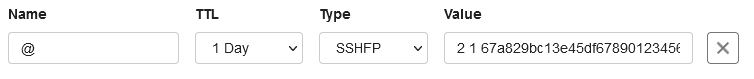
Name
You set up an SSHFP record by starting with the name. This is where you specify for which part of the domain the DNS record should work. An SSHFP record can be set for both the root domain and for subdomains.
- If you want to set an SSHFP record for the root domain, enter an @ in the 'Name' field.
- If you want to set an SSHFP record for a subdomain, only enter the subdomain in the 'Name' field.
- Our DNS software will automatically add the root domain name in the background.
TTL
The 'TTL' of a DNS record determines how long the record can remain in the cache. We recommend keeping the TTL low, for example at 1 hour.
Type
Because you wish to set an SSHFP record, choose 'SSHFP' under 'Type'.
Value
In the 'value' field of the SSHFP record you consecutively enter the algorithm, fingerprint type, and the fingerprint, separated by spaces.
We use the image below as an example:

- The algorithm (2), which stands for DSA
- The fingerprint type (1), which stands for SHA-1
- The fingerprint (67a829bc13e45df67890123456789abcdef67890)
We will further explain the three elements below.
Algorithm
The 'value' of the SSHFP record starts with a number (1, 2, 3, or 4) which indicates which algorithm is used by the public key.
- RSA
- DSA
- ECDSA
- Ed25519
Fingerprint type
The second number of the 'value' is either 1 or 2, which represents the type of algorithm used to generate the public key's fingerprint.
- SHA-1
- SHA-256
Fingerprint
After the first two numbers which represent the algorithms used for the public key and its fingerprint, you add the fingerprint itself. The fingerprint is the hash result of the SSH key, expressed in hexadecimals (characters '0-9' and 'a-f').
SHA-1 fingerprints have a length of 40 characters, SHA-256 fingerprints consist of 64 characters.
In this article we explained how to set SSHFP records in your controle panel. For a general explanation about DNS records and entering them, see the article ‘DNS and nameservers'.




